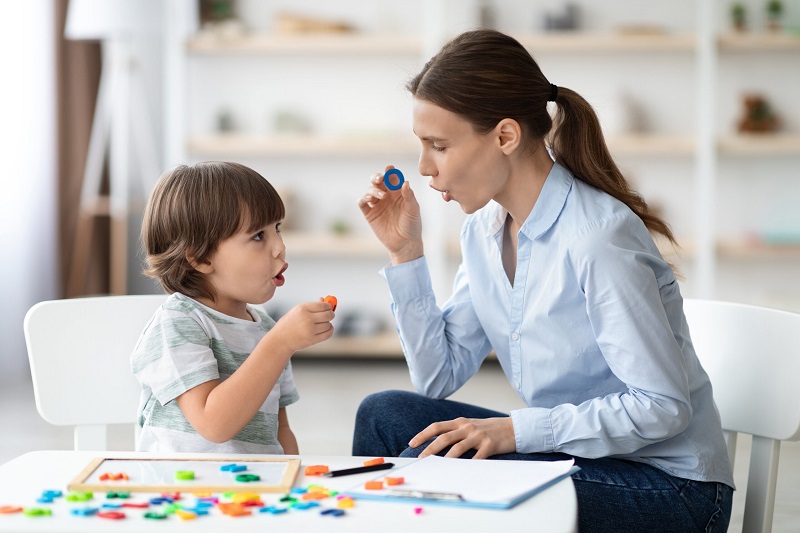
Autism is a complex neurodevelopmental condition that presents unique challenges for individuals, impacting various aspects of their lives. One of the defining characteristics of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is the difficulty in navigating social interactions, communicating effectively, and exhibiting repetitive behaviors. These challenges can manifest differently from person to person, making autism a spectrum disorder with a wide range of presentations and symptoms.
When it comes to communication, individuals with autism often encounter obstacles that affect their ability to express themselves and understand others. These difficulties can encompass both verbal and nonverbal communication skills. Some individuals may struggle with spoken language, finding it hard to articulate their thoughts and feelings or to grasp the meaning of spoken words. Others may face challenges in nonverbal communication, such as maintaining eye contact, interpreting facial expressions, or understanding gestures and body language.
In this article, we aim to delve deeper into the intricate world of speech challenges in autism, exploring the various factors that contribute to these difficulties and discussing potential strategies for support and intervention. By gaining a better understanding of the nuances of speech challenges in autism, we can provide more effective support and empower individuals on the autism spectrum to communicate more confidently and successfully in their daily lives.
Definition of Autism
Autism, or ASD, is a complex developmental condition that typically manifests in early childhood and persists throughout a person’s lifetime. It is characterized by a spectrum of challenges, including social difficulties, repetitive behaviors, and communication impairments.
Importance of Speech-Language Pathologists (SLPs) in Autism
Speech-Language Pathologists play a crucial role in assessing, diagnosing, and treating communication difficulties in individuals with autism. Their expertise is instrumental in addressing the unique needs of each person on the autism spectrum, fostering improved communication skills and quality of life.
Common Speech Challenges in Autism
Echolalia
Echolalia, the repetition of words or phrases spoken by others, is a common speech characteristic observed in individuals with autism. While it can serve various communicative functions, such as expressing wants or needs or processing language, it may also present challenges in spontaneous and meaningful communication.
Pronoun Reversal
Pronoun reversal, wherein individuals with autism may refer to themselves or others using incorrect pronouns (e.g., saying “you” instead of “I”), is another prevalent speech challenge. This difficulty in understanding and using pronouns can impact social interactions and hinder effective communication.
Prosody Difficulties
Prosody refers to the rhythm, intonation, and stress patterns in speech that convey emotional and linguistic nuances. Many individuals with autism experience challenges in modulating prosody, leading to flat or monotone speech, difficulties in conveying emotions, and misunderstandings during social interactions.
Factors Contributing to Speech Challenges
Sensory Sensitivities
Sensory sensitivities are common in autism and can significantly impact speech and language development. Hypersensitivity or hyposensitivity to auditory, tactile, or visual stimuli may affect an individual’s ability to attend to and process speech sounds, leading to communication difficulties.
Motor Planning Issues
Motor planning refers to the ability to plan, sequence, and execute movements, including those involved in speech production. Many individuals with autism experience challenges in motor planning, which can manifest as articulation difficulties, stuttering, or apraxia of speech, further complicating communication.
Social Communication Differences
Differences in social communication, such as challenges in understanding nonverbal cues, initiating and maintaining conversations, and perspective-taking, can also contribute to speech difficulties in autism. These social communication deficits may affect pragmatic language skills and hinder effective communication in various contexts.
Assessment and Diagnosis
Standardized Assessments
Speech-Language Pathologists use standardized assessments, such as the Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule (ADOS) and the Childhood Autism Rating Scale (CARS), to evaluate communication skills and identify speech challenges in individuals with autism. These assessments help inform diagnosis and treatment planning.
Observation and Interaction
In addition to standardized assessments, SLPs rely on careful observation and interaction with individuals with autism to assess their speech and language abilities in real-life contexts. This hands-on approach allows SLPs to gain valuable insights into the individual’s communication strengths and challenges.
Collaboration with Multidisciplinary Team
Collaboration with a multidisciplinary team, including educators, psychologists, and other professionals, is essential in assessing and diagnosing speech challenges in autism comprehensively. By working together, the team can develop a holistic understanding of the individual’s needs and tailor interventions accordingly.
Treatment Approaches
Augmentative and Alternative Communication (AAC)
For individuals with limited verbal communication abilities, augmentative and alternative communication (AAC) systems, such as picture symbols, communication boards, or speech-generating devices, can provide alternative means of expressing thoughts, feelings, and desires.
Social Communication Interventions
Social communication interventions, such as Social Stories, video modeling, and peer-mediated strategies, aim to improve social interaction skills and pragmatic language abilities in individuals with autism. These interventions focus on teaching social norms, turn-taking, conversational skills, and perspective-taking.
Sensory Integration Therapy
Sensory integration therapy, which involves structured activities designed to regulate sensory processing and promote adaptive responses to sensory stimuli, may benefit individuals with autism who experience sensory sensitivities impacting speech and language development. By addressing sensory challenges, this therapy can support improved communication outcomes.
In conclusion, understanding the speech challenges in autism requires a multifaceted approach that considers the unique strengths, needs, and experiences of each individual. Speech-Language Pathologists play a pivotal role in this process, offering insights, assessments, and interventions aimed at fostering effective communication and enhancing quality of life for individuals on the autism spectrum. Through collaborative efforts and evidence-based practices, we can empower individuals with autism to reach their full communicative potential and thrive in their social interactions and relationships.
Are you interested in delving into the treatment and management of special needs children with developmental disorders? Look no further than Nurture Pods’ free online course. This comprehensive offering aims to equip you with the necessary knowledge and skills to effectively engage with children facing conditions like Autism, ADHD, and anxiety disorder.
Throughout the course, we’ll explore the unique characteristics and common challenges experienced by children with such conditions. Understanding these nuances is essential for providing tailored support and assistance. Moreover, we’ll delve into proven techniques for managing these children in various scenarios.
One such technique is Applied Behaviour Analysis (ABA), renowned as the gold standard for treating Autism. This evidence-based approach focuses on understanding and modifying behaviors to promote positive outcomes. By incorporating ABA principles into your interactions, you can make a meaningful difference in the lives of children with Autism and other developmental disorders.
Written by: Alex Liau
Published on 11 March 2024